Description
This document describes the requirements for using level crossings.
Not what you are looking for? See more NGE Rules
Purpose
To prescribe the rules for using level crossings in the Network.
Principle
Level crossings are high risk areas where rail traffic crosses paths with road and pedestrian traffic at the same level.
Qualified Workers in charge of level crossings must ensure the safety of rail, road and pedestrian traffic.
Missing, damaged or faulty equipment or gates at a level crossing must be reported to the Signaller.
The Signaller must treat the report as a Condition Affecting the Network (CAN).
The Network Controller must arrange for the Maintenance Representative to be told about the CAN.
If active control warning equipment at a road or pedestrian level crossing is faulty, the Network Controller must arrange, as necessary, for Handsignallers to protect the level crossing.
Types of level crossings
Road and pedestrian traffic is warned by active or passive control warning equipment.
Active control uses one or more of lights, booms, gates, audible warning devices or lit signs to warn that rail traffic is approaching a level crossing.
Passive control uses only signs to warn about the presence of a level crossing.
The following types of level crossings are used in the Network:
- Type B level crossings with GIVE WAY roadside warning signs immediately before the level crossing
- Type D level crossings with STOP roadside warning signs immediately before the level crossing
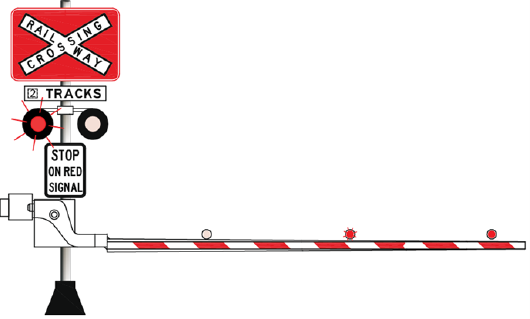
- Type F level crossings, with roadside flashing lights and audible warning devices, and with or without booms
- level crossings with manually operated gates
- Network access level crossings
- pedestrian level crossings
- private level crossings.
Pedestrian level crossings
Pedestrian traffic is controlled by one or more of:
- walkway warning signs
- crossing approach mazes
- audible warning devices
- lit DON’T WALK displays
- lit STOP displays
- lit arrows showing the direction of approach of rail traffic
- automatically or manually controlled gates or booms.
Pedestrian level crossings might be associated with road level crossings.
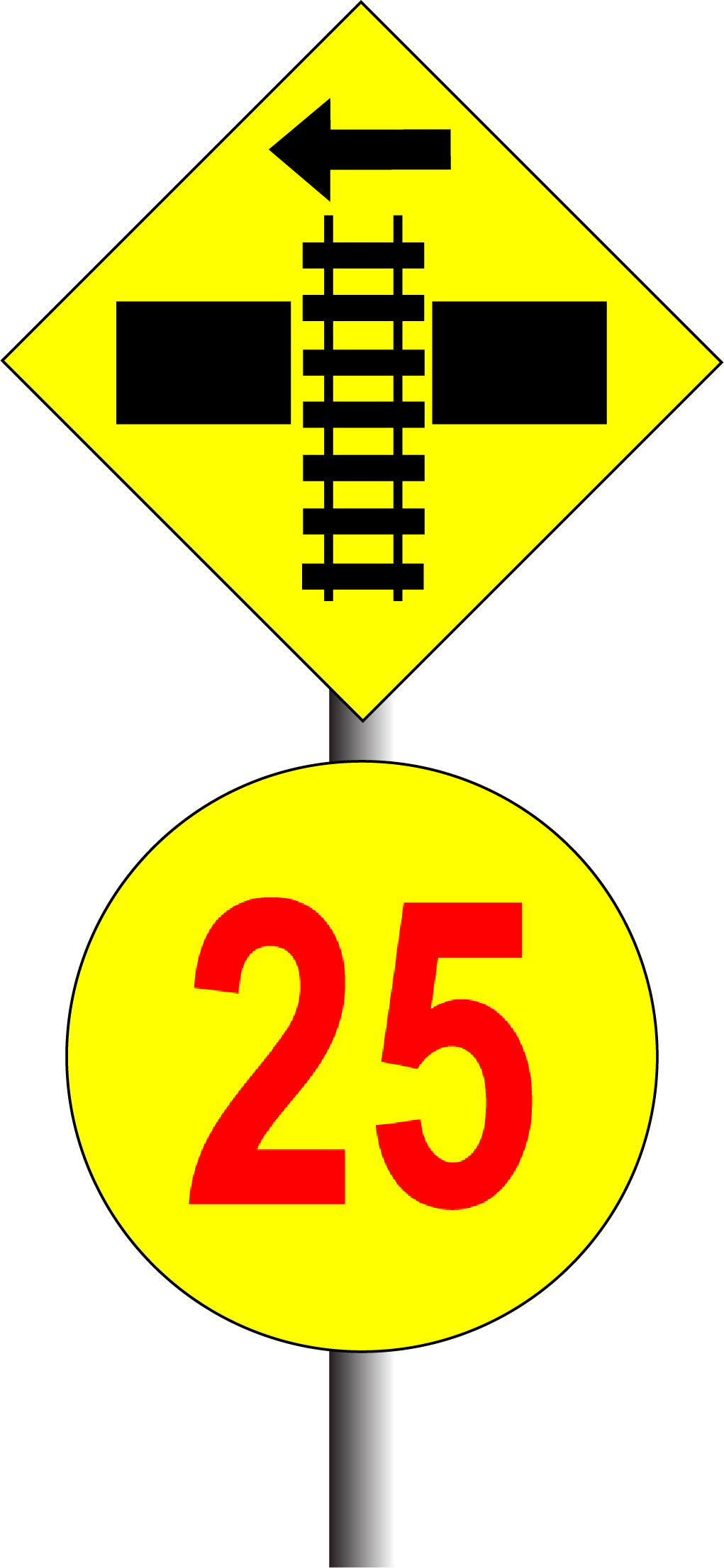
Level crossing speed signs
Level crossing speed signs are placed in the approach to level crossings with reduced visibility.
Rail traffic must not exceed the indicated speed during approach to the level crossing.
After the leading vehicle has fully cleared the level crossing, rail traffic may resume normal speed.
Conditional level crossing speed signs
If the visibility of a level crossing can be reduced by adjacent rail traffic beyond the sign, a conditional level crossing speed sign is placed in the approach to the level crossing.
Rail traffic must not exceed the indicated speed during approach to the level crossing.
After the leading vehicle has fully cleared the level crossing, rail traffic may resume normal speed.
Type F level crossings
Type F level crossing roadside warning equipment may be operated automatically by track-circuit, or be controlled by Qualified Workers.
Some Type F level crossings are equipped with predictor circuitry that senses and responds to the speed of approaching rail traffic.
Type F level crossing trackside signs
Trackside signs before standard Type F level crossings mark the start of controlling track-circuits.
Rail traffic must not accelerate between the trackside sign advising approach to a Type F level crossing fitted with predictor circuitry and the level crossing.
If rail traffic stops within the predictor circuitry, the type F level crossing roadside warning equipment may deactivate. After resuming travel Drivers and Track Vehicle Operators must:
- stop short of the level crossing warning equipment to check if the warning equipment is operating correctly, and
- proceed over the level crossing only if it is safe to do so, and
- not exceed 25km/h before the leading vehicle has cleared the crossing.
Type F level crossing roadside warning equipment
Type F level crossing roadside warning equipment includes:
- advance warning signs
- bells or other audible warning devices
- flashing lights.
The warning equipment might also include:
- advance warning lights for road users
- half-booms or full-booms for road users
- booms or gates for pedestrians
- warning lights for pedestrians.
Level crossings with manually operated gates
Manually operated gates close across the track, the road or the walkway.
Roadside warning signs warn road and pedestrian traffic.
Unattended locations
At unattended locations other than private level crossings, Qualified Workers, train crews or track vehicle crews must make sure that manually operated gates are:
- closed across roads and walkways before rail traffic uses the level crossing, and
- re-opened to road and pedestrian traffic only after rail traffic has fully cleared the level crossing.
Attended locations
Gates at attended locations must have a steady red light during darkness and in conditions of low visibility.
Signallers must clear signals allowing approach to a level crossing with manually operated gates only after making sure that the gates have been closed across roads and walkways.
Signallers must authorise the re-opening of gates to road and pedestrian traffic.
Before leaving a location unattended, Signallers must make sure that signals protecting level crossings with manually operated gates are set at STOP.
Network access level crossings
Network access level crossings are usually permanent crossings provided at authorised locations for Network maintenance.
Some Network access level crossings have passive or active control warning equipment.
Temporary level crossings may be established for Network maintenance. Possession Protection Officers and Protection Officers are responsible for the safety and protection of temporary level crossings used during maintenance work.
Absolute Signal Blocking or a work on track authority must be implemented to allow vehicles to cross the track at designated network access level crossings, unless:
- special instructions are specified in the Network Local Appendix, or
- the network access level crossing is fitted with passive control or active control warning equipment.
Private level crossings
Private level crossings allow private access across Network tracks. Private level crossings may have:
- manually operated gates
- roadside signs.
Qualified Workers who notice open gates at private level crossings must tell the Signaller. The Signaller must tell a Maintenance Representative.
Roadside warning signs
The following signs warn road users and pedestrians about level crossings.