Description
This document describes the procedure for planning, implementing and managing a Track Occupancy Authority (TOA).
Not what you are looking for? See more Procedures
Introduction
Track Occupancy Authorities (TOA) are used to occupy a defined portion of track within specified limits for an agreed period.
A TOA may:
- allow the track to be broken or obstructed
- allow rail traffic associated with the TOA to work within the specified limits
- be granted for track vehicles to travel singly or in convoy.
The preferred method of obtaining a TOA is to take and safeguard the pilot staff or half-staff where practicable.
Where the limits of a TOA extend into the yard limits controlled by another Signaller, the affected Signallers must confer to make sure all points of entry are protected.
Joint occupancy following a unidirectional rail traffic movement
A TOA may be authorised following a unidirectional rail traffic movement.
Protection Officer
- Identify the line name and define the limits of the worksites or the location of road/rail access points as being between two signals.
Signals must be identified by their numbers.
If the limits of the worksites need to be defined for multiple worksites, a signal before the first worksite and a signal after the last worksite must be used.
- For track vehicle travel, identify the direction of travel.
Signaller
- Use the reference points provided by the Protection Officer to identify the limits of worksites or the location of road/rail access points.
Joint occupancy with disabled rail traffic
A TOA may be authorised for a portion of track occupied by disabled rail traffic.
Signaller
- Restrain all disabled rail traffic within the proposed limits of the TOA.
- Make sure that the disabled rail traffic will not be moved before authority is obtained from the Protection Officer.
Joint occupancy with stabled rail traffic
The limit of a TOA may be authorised to include one or more sidings occupied by stabledrail traffic.
Signaller
- Make sure that the Protection Officer will place protection to prevent the unintended movement of the stabled rail traffic.
- If known, tell the Protection Officer the scheduled departure time of stabled rail traffic.
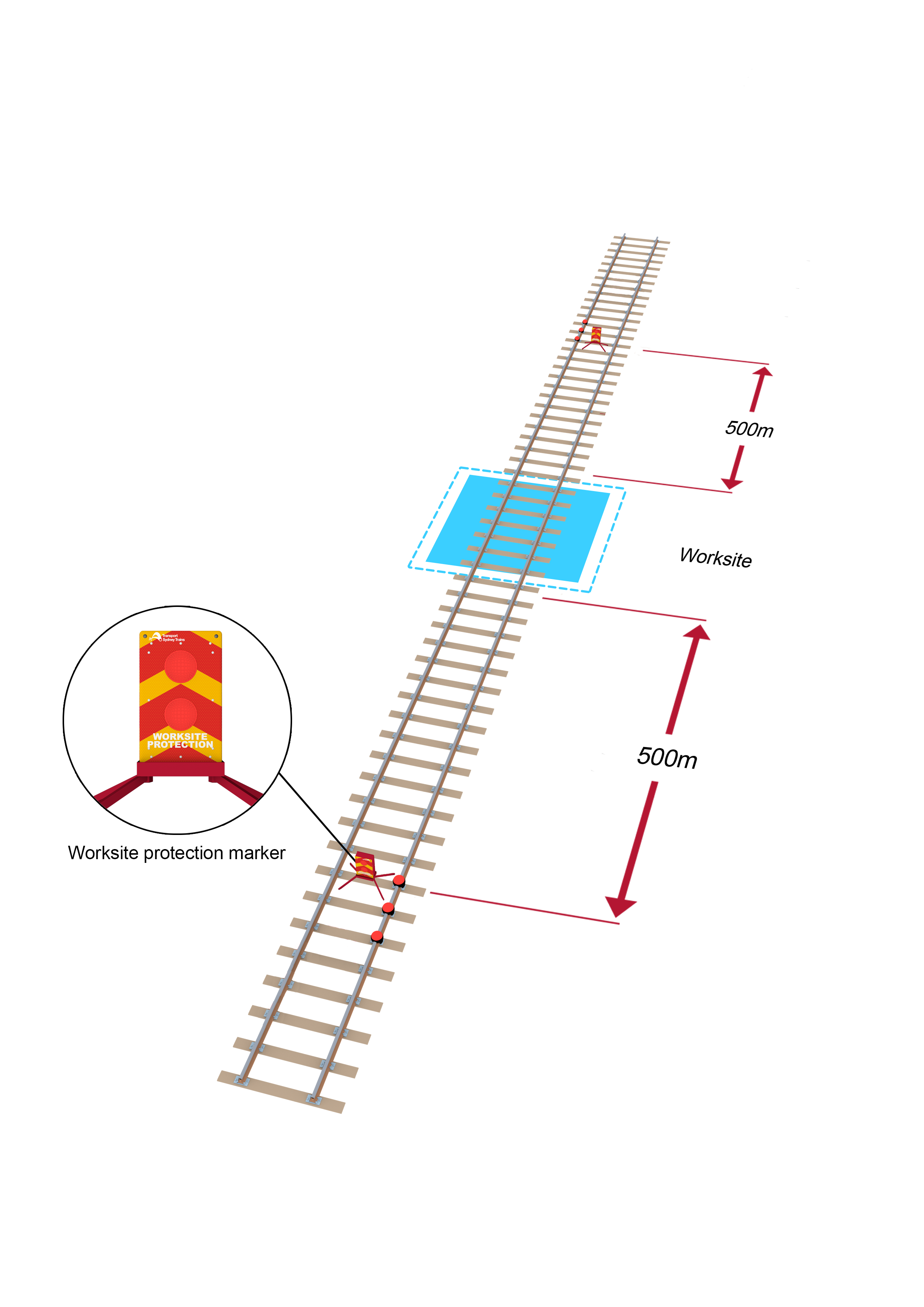
Protecting worksites
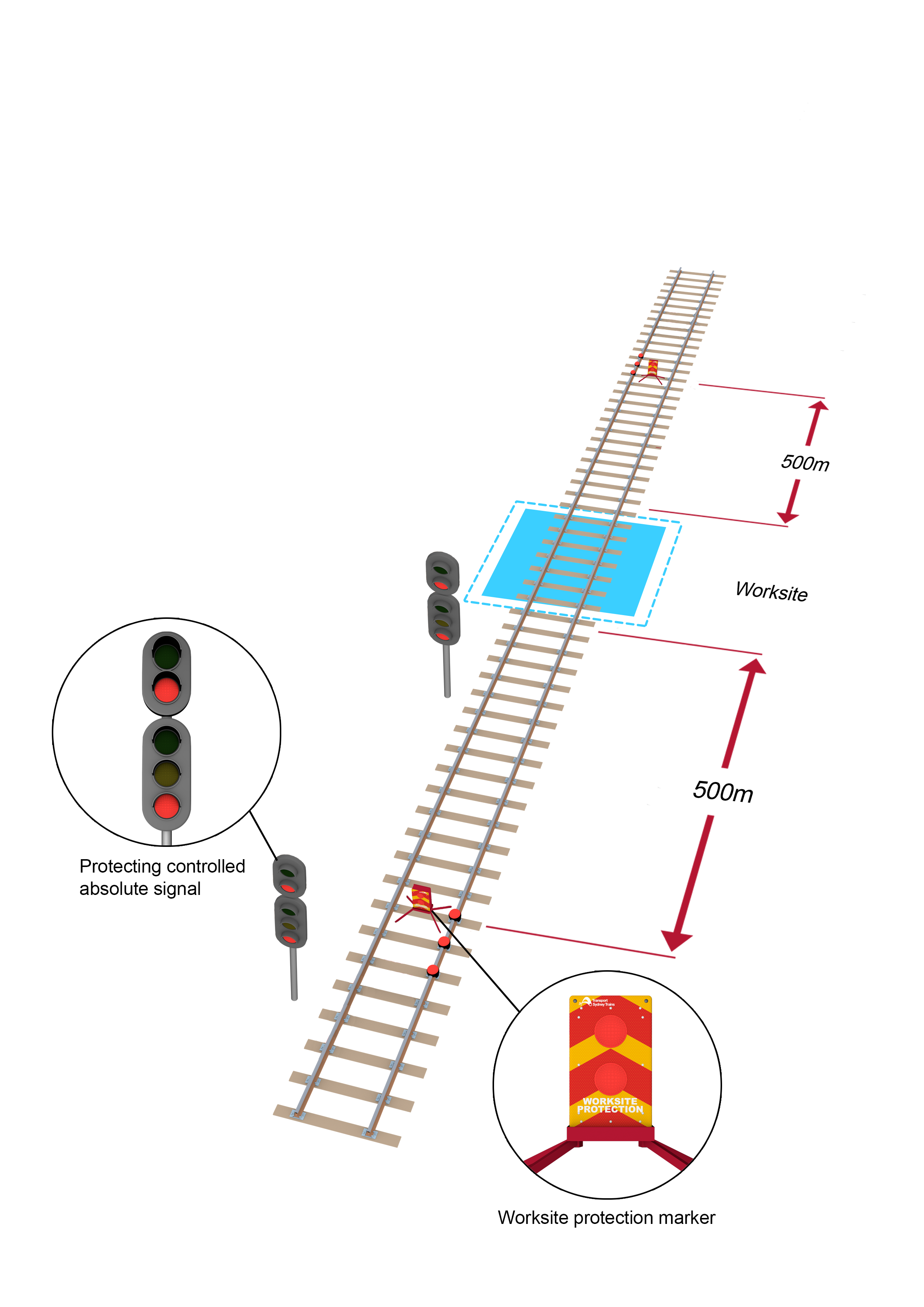
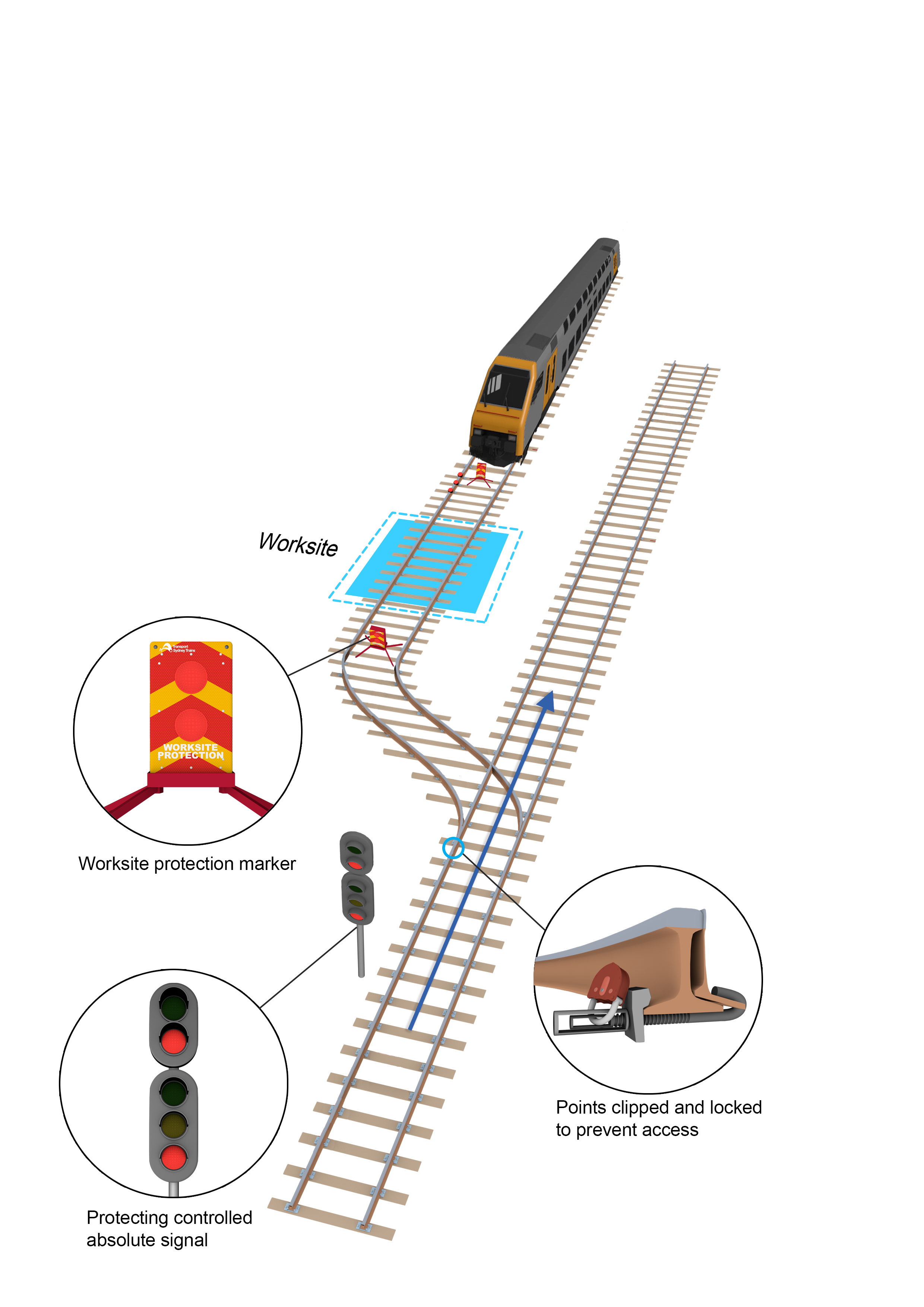
When using railway track signals, make sure that worksite protection markers are placed in the middle of the four-foot, adjacent to the railway track signal closest to the worksite.
Protection Officer
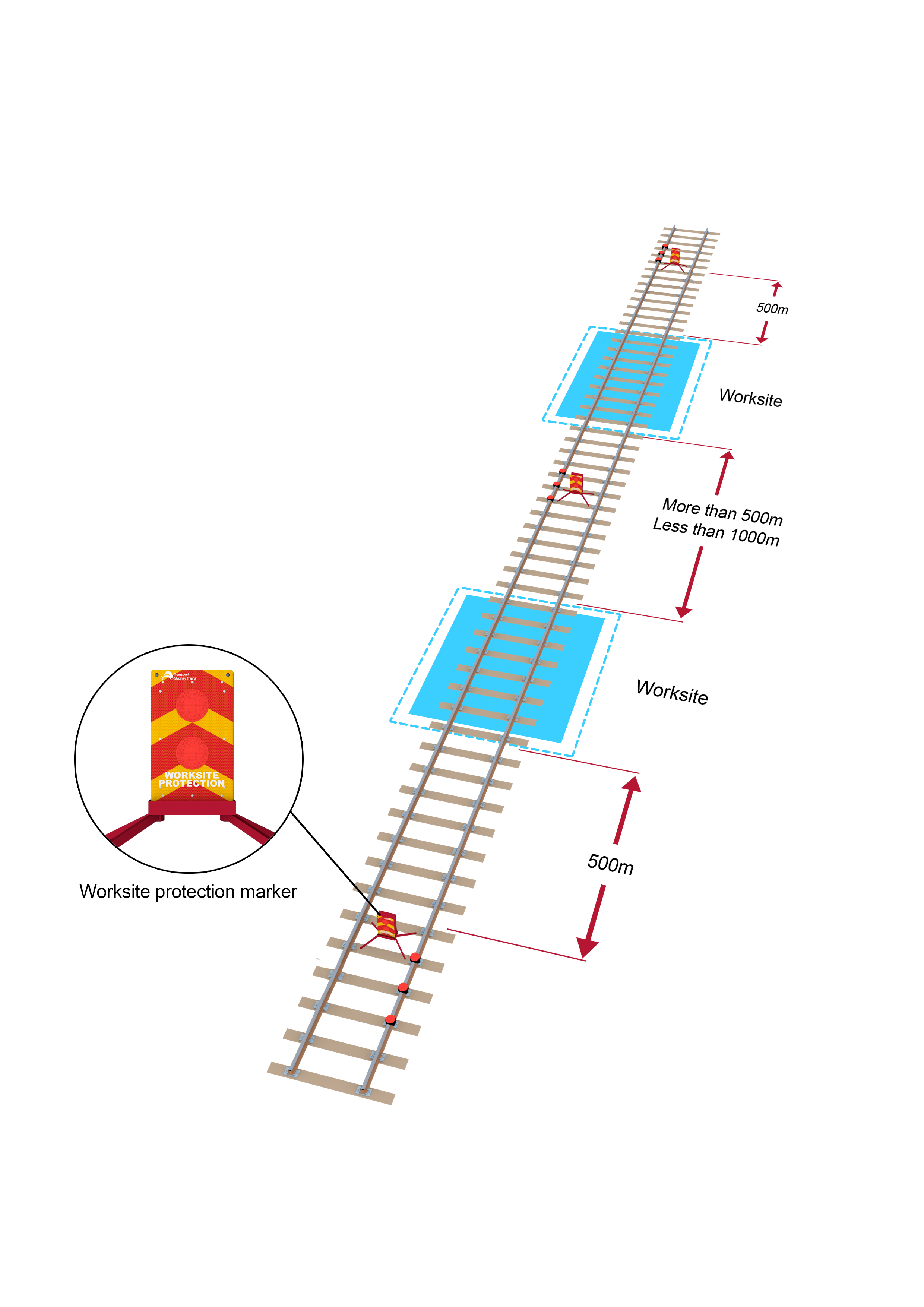
- If required, place three railway track signals and a worksite protection marker between 500m and 1000m from the worksite.
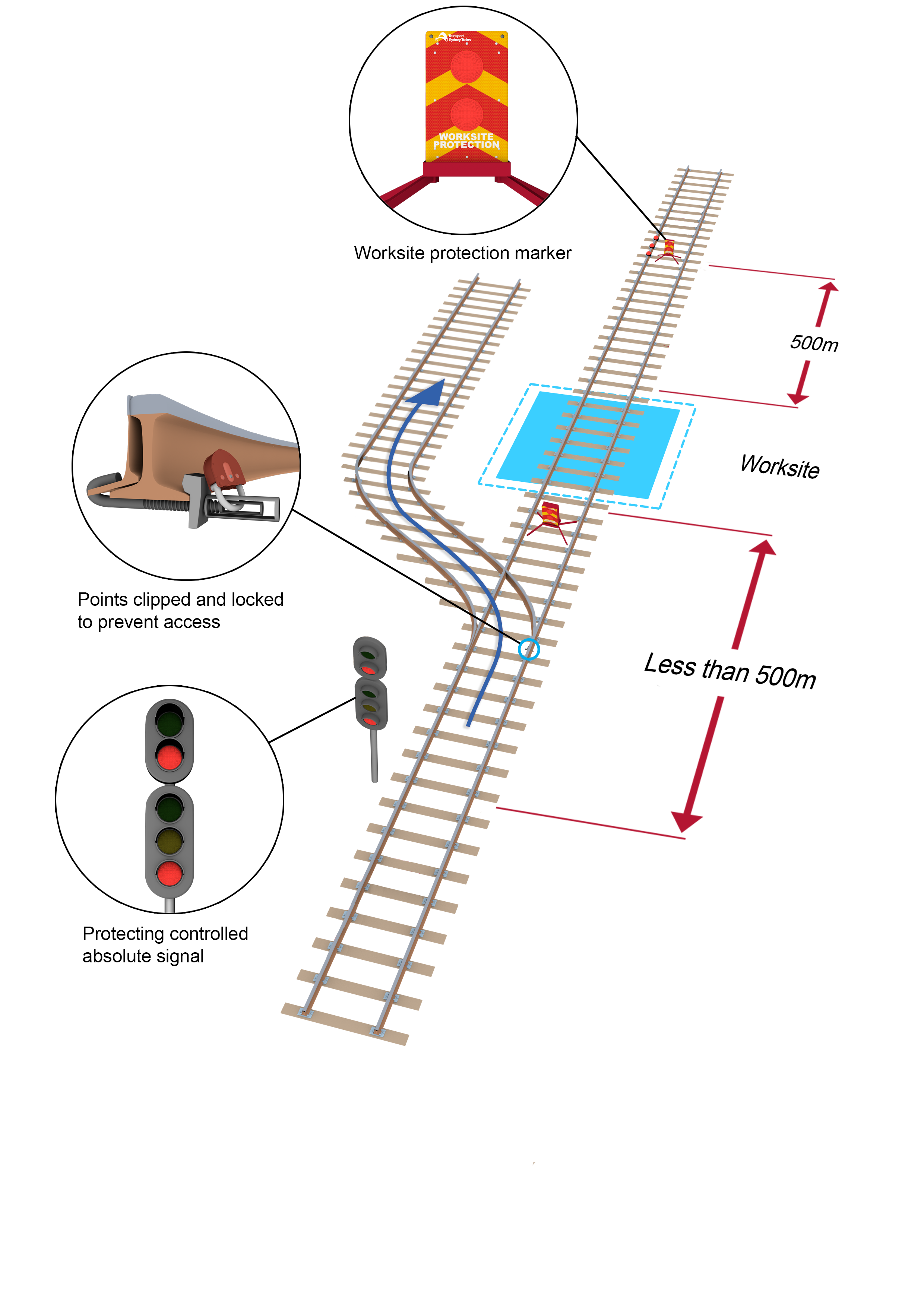
- If a controlled absolute signal is within 500m of the worksite, a controlled absolute signal more than 500m from the worksite must be used for worksite protection.
- If a controlled absolute signal less than 500m from the worksite is used to prevent access to the portion of track within the TOA limits, and a set of points is available for a different route, then clip and lock the points for the different route.
- If points cannot be clipped and locked for a different route, use a controlled absolute signal more than 500m from the worksite.
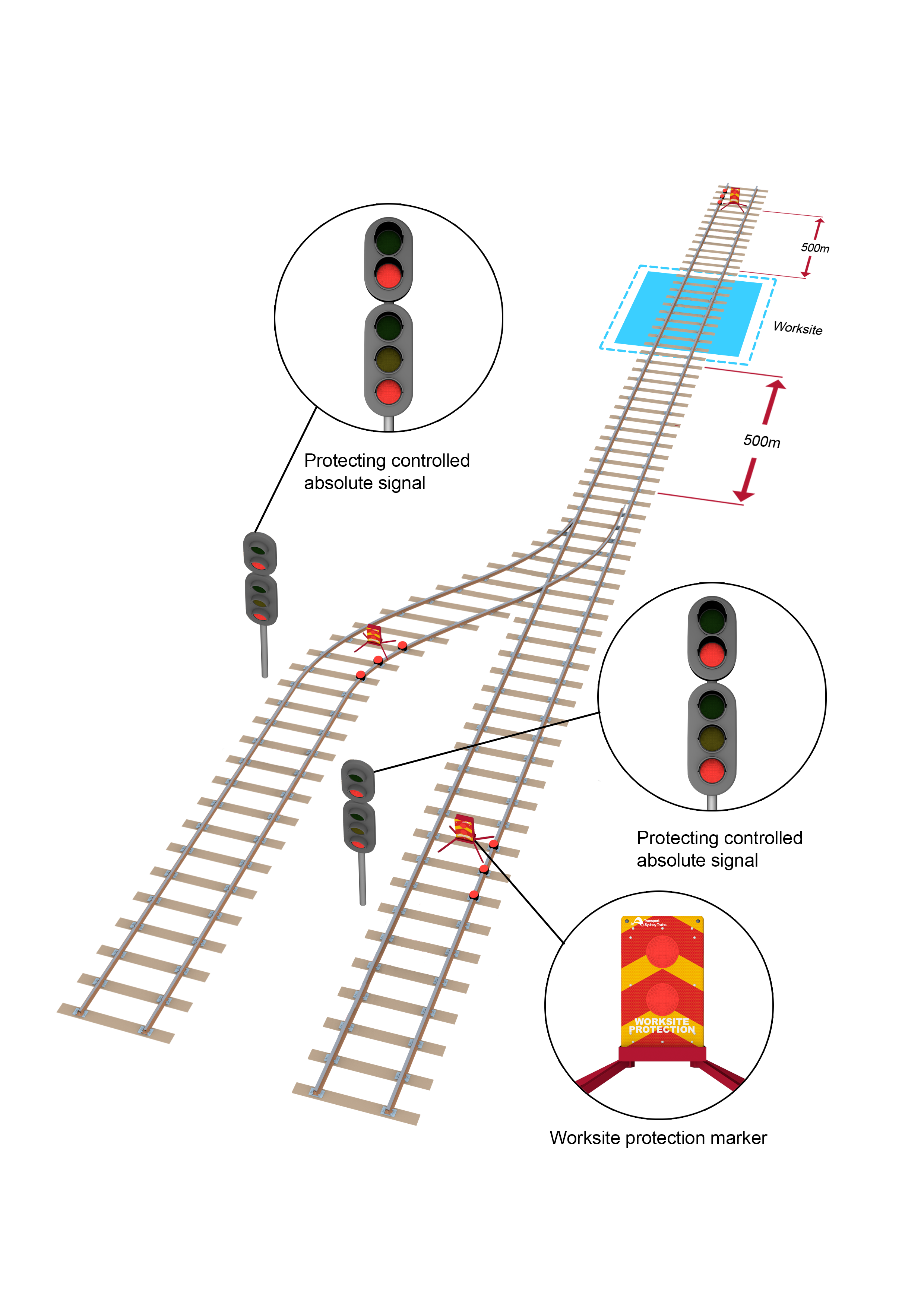
- Where multiple worksites are located within the TOA limits or additional work on track authorities have been authorised, three railway track signals and a worksite protection marker must be placed between 500m and 1000m from the entry end of each worksite.
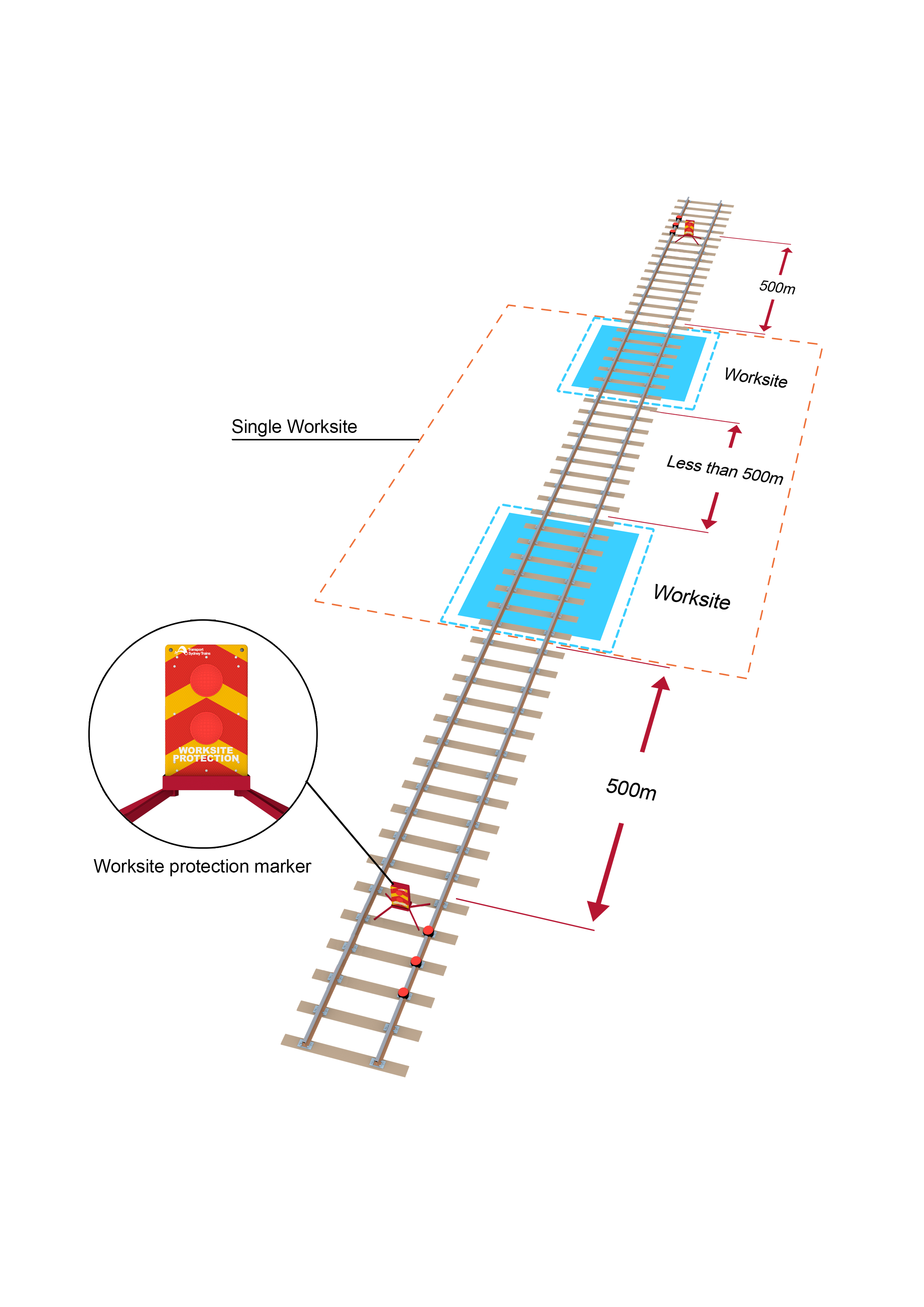
If worksites are between 500m and 1000m apart, three railway track signals and a worksite protection marker must be placed midway between the worksites.
- Worksites less than 500m apart must be protected and managed as a single worksite.
- If stabled rail traffic within a siding is not associated with the TOA, three railway track signals and a worksite protection marker must be placed immediately in front of the stabled rail traffic to prevent unintended movements within the TOA.
The worksite protection marker must be placed next to the railway track signal closest to the stabled rail traffic and in a position that can be seen from the stabled rail traffic.
Obtaining an extension of time for a TOA
Protection Officer
- If necessary, ask the Signaller for an extension of time for the TOA.
- When an extension is authorised, record the new expiry time and the authorising Network Controller’s name on the TOA form.
Signaller
- Tell other affected Signallers about the new expiry time for the TOA.
Returning the track to service
Protection Officer
- Make sure that rail traffic and equipment are clear of the Danger Zone.
- Make sure that all workers have cleared the worksites.
- Make sure that:
- point clips have been removed
- railway track signals and worksite protection markers have been removed
- if necessary, signals have been restored to normal use
- the track is safe for use.
- If necessary, when advised that the line is certified fit for use, tell the Signaller.
- Tell the Signaller that the work is complete and about any restrictions on track use.
- If removed, replace the half-staffs, as required by the Signaller.
- Fulfil the TOA.
Signaller
- Confirm with the Protection Officer:
- their name
- the worksite location
- the TOA number
- that workers and equipment are clear of the Danger Zone
- that, if used:
- half-staffs have been restored
- points that were clipped and locked are available for use
- that the TOA is fulfilled.
- Remove blocking facilities.
- Test signals affected by half-staffs.
- Tell the Network Controller that the TOA is fulfilled, and about any restrictions on track use.
Keeping records
Network Controllers, Signallers and the Protection Officer must record, in permanent form, the TOA details, including protection arrangements.